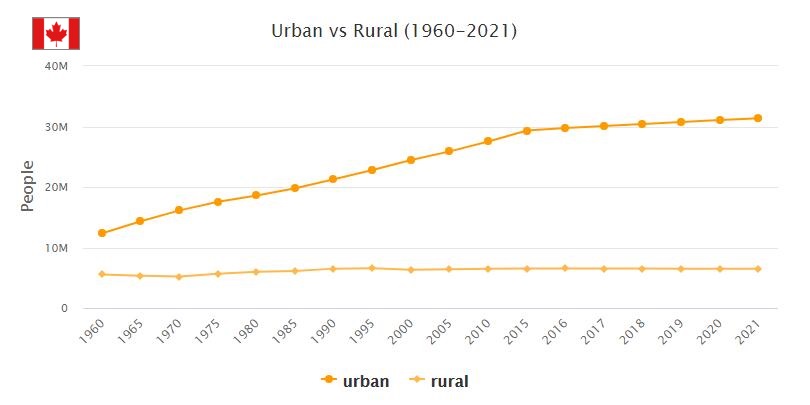
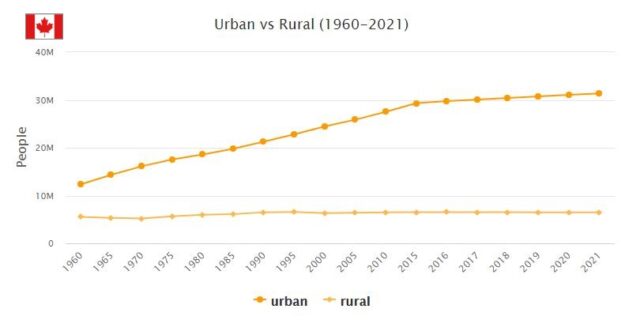
Canada is a North American nation located in the northern portion of the continent with a population of over 37 million people. The majority of the population is ethnically diverse, comprised of numerous indigenous tribes, with notable minorities of French and British-speaking people. Christianity is the predominant religion, with over 60% of citizens identifying as Roman Catholics while the remaining 40% are followers of other religious groups. The official languages are English and French, but numerous Indigenous languages are also commonly spoken. Most Canadians live in urban areas and work in industry or services rather than agriculture. Poverty levels have been steadily decreasing since 2010, with the unemployment rate currently at 5%. Check hyperrestaurant to learn more about Canada in 2009.
Social conditions
Social conditions vary greatly between the different provinces. The legislation also gives room for the provinces to design their own subsidy schemes, etc. However, because the welfare system has tended to grow sharply, especially since the 1960s, the provinces have had difficulty managing their own funding. A large part of the social sector is therefore financed with federal funds, and this helps to offset the sharp differences in income between the provinces.
The Canadian general health insurance covers all health care that residents may need. Visit AbbreviationFinder to see the definitions of CDA and acronym for Canada. It differs somewhat in detail between different provinces, some of which take out sickness insurance in general tax, others use a progressive compulsory insurance premium. The federal government supports the provincial health care costs through grants. Healthcare is of a very high class, at costs lower than in the United States. Very large resources are devoted to providing adequate healthcare to the northern parts of the country. Despite this, Indigenous peoples have First Nations and Inuit people in poorer health than in the rest of the country due to modern well-being illnesses and social problems such as alcoholism, unemployment and crime. Check to see Canada population.
Child allowance is paid to all children under the age of 18. However, the provinces determine the design, so that in some provinces the amount becomes higher the older the children become. Childcare consists of nursery schools for the youngest children, day care centers for 3- and 4-year-olds and kindergarten for 5-year-olds. The first two institutions are usually private or cooperative, while the latter is a preschool where most children attend.
Since 1970, unemployment insurance covers all employees and has gradually become more extensive. It also includes pregnancy and health care benefits and is funded by employees, employers and federal funds. Social grants can be obtained by anyone who “needs” it. This need is carefully examined in each case, and the grant is paid only when no other possibilities, e.g. unqualified work, remains. There is a strong social pressure against grant dependency. Because of these factors, there is an extensive charity system with, among other things, clothing and food collections.
The pension system covers old-age pension (starting at age 65), early retirement and widow’s pension. It consists partly of a mainly federally funded minimum compensation and partly of a general occupational pension, which today includes most employees. The pensions are index-regulated.
Canada has always had laws and programs to protect the indigenous population, programs that, in tandem with increasing political awareness, have been administered by First Nations and the Inuit’s own organizations. Special resources are invested in healthcare, housing, education and social care for Inuit and First Nations. Individuals from the indigenous population who are outside the tribal organization often face social difficulties, as they do not benefit from the federal programs.
Country data
Area: 9,984,670 km2 (world ranking: 2)
Residents: 36,708,000
Population density: 4 per km2 (as of 2017, world ranking: 38)
Capital: Ottawa
Official languages: English, French
Gross domestic product: 1,653 billion US $; Real growth: 3.0%
Gross national product (GNP, per resident and year): 42,870 US $
Currency: 1 Canada. Dollar (kan $) = 100 cents
Embassy
Leipziger Platz 17, 10117 Berlin
Phone 030 203120,
Fax 030 20312590
www.kanada-info.de
Government
Head of State: Elizabeth II, Head of Government: Justin Trudeau, Exterior: Christina Alexandra “Chrystia” Freeland
National holiday: 1.7.
Administrative organization
10 provinces and 3 territories under federal administration
State and form of government
Constitution of 1982
Federal parliamentary monarchy (in the Commonwealth)
Parliament: House of Commons (Chambre des Communes) with 338 members, election every 4 years; Senate (Senate / Sénat) with 105 members (appointed by the Governor General on the proposal of the Prime Minister)
Suffrage from 18 years.
Population: Canadians, last count 2016: 35,151,728 residents
32% Canadian, 18% English, 14% Scottish, 14% French, 13% Irish, 10% German, 6% indigenous (First Nations, Inuit and Métis), 5% Chinese, 5% Italian descent and others
Cities (with population): (as of 2016) Toronto 2,731,571 inh. (A 5.9 million), Montréal 1,704,694 (A 4.1 million), Calgary 1,239,220 (A 1.4 million), Ottawa 934,243 (A 1.3 million), Edmonton 932,546 (A 1.3 million), Mississauga 721,599, Winnipeg 705,244, Vancouver 631,486 (A 2.5 million), Brampton 593,638, Hamilton 536,917, Québec 531,902, Surrey 517,887, Laval 422,993, Halifax 403,131, London 383,822, Markham 328,966, Vaughan 306,233, Gatineau 276,245, Saskatoon 246,376, Longueuil 239,700
Religions: 67% Christians (39% Catholics, 22% Protestants etc.), 3% Muslims, 2% Hindus, 1% Sikhs, 1% Jews, 1% Buddhists; 24% without religion (as of 2006)
Languages: (as mother tongues) 56% English, 21% French, 21% other languages (Chinese, Italian, German, Punjabi, Spanish as well as indigenous languages, etc.)
Employed by economic sector: Agriculture. 2%, industry 20%, business. 78% (2017)
Unemployment (in% of all labor force): 2017: 6.3%
Inflation rate (in%): 2017: 1.6%
Foreign trade: import: 132.4 billion US $ (2017); Export: US $ 420.4 billion (2017)
Ottawa
Ottawa, the capital of Canada; 883,000 homes (2001), in the Ottawa-Hull metropolitan area 1.24 million. The city is located on the Ottawa River in eastern Ontario and is connected by bridges to the neighboring town of Hull in Quebec. It was built under the name Bytown in 1826 in connection with the construction of the Rideau Canal (with connection to Lake Ontario), but changed its name in 1855 and became the capital of the state in 1867.
Ottawa is characterized by the central administration as well as universities and a large number of museums and federal institutions, such as the National Arts Center (theater, opera, concert hall), the National Gallery of Canada (with extensions (1988) by Moshe Safdie) and the impressive Musée Canadien des Civilizations in Hull. The 1800’s timber and paper industries have almost disappeared and been replaced by high tech industries as well as banking, insurance and publishing companies.
After an extensive renovation of the city center in particular, which has been on a regular basis since the 1920’s, Ottawa appears beautiful and clean with a marked set of parks and trails. The city’s landmark is the Parliament Building with the Peace Tower by the 8 km long Rideau Canal, which in winter is used as a popular ice rink through the city. Establishing a light rail system, the Ottawa Light Rail Project, started in 2001. Together with foreign representations and a growing minority of Lebanese and Chinese, the many tourists give the city a cosmopolitan atmosphere.