Chile is a South American nation located in the western portion of the continent with a population of over 18 million people. The majority of the population is ethnically diverse, comprised of numerous indigenous tribes, with notable minorities of German and Italian-speaking people. Christianity is the predominant religion, with over 70% of citizens identifying as Roman Catholics while the remaining 30% are followers of other religious groups. The official language is Spanish, but Mapudungun and numerous other indigenous languages are also commonly spoken. Most Chileans live in urban areas and work in industry or services rather than agriculture. Poverty levels have been steadily decreasing since 2010, with the unemployment rate currently at 6%. Check hyperrestaurant to learn more about Chile in 2009.
Social conditions
The highly market-driven, neo-liberal economic policies pursued in Chile after the 1973 military coup had led to a competitive economy – by Latin American dimensions – at the end of the 1980s, but also to sharply increasing social divisions. Visit AbbreviationFinder to see the definitions of CHL and acronym for Chile. After the democratization in 1990, the rate of growth has remained high. The pay gap is large between different groups in society, and about 15 percent of the population lives below the national poverty line.
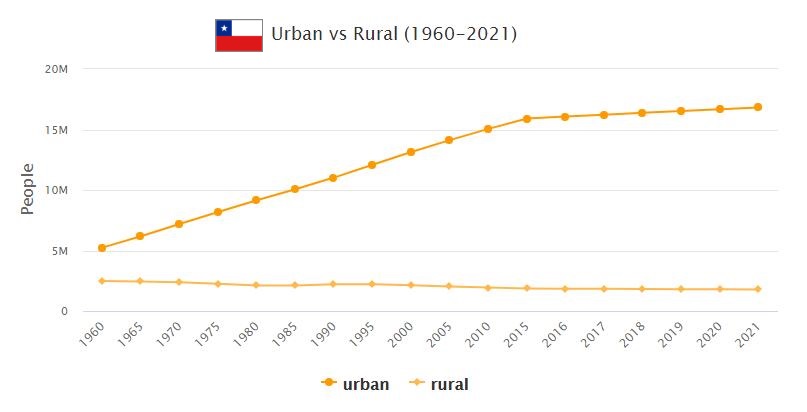
After an economic crisis around 1982, growth has been particularly strong in export-oriented sectors of the agricultural, forestry and fisheries industries. This development has slowed down the move into cities. However, the population is highly concentrated in the central parts of the country, around the capital Santiago. Check to see Chile population.
After 1973, unemployment increased dramatically. However, economic growth has led to increased employment and continuously falling unemployment figures since the crisis in 1982. Unemployment, according to official figures in 2012, was around 6 percent. At the same time, real wage developments, especially after 1991, have been favorable. Large resources have been invested in housing construction programs for the poorer population strata.
In parallel with the development of neoliberal economic policy, the legislation governing the labor market was eroded and was considered to be more advanced in Latin America. Important reforms of both job protection and the rules of trade union organization and collective bargaining have taken place since 1990, but the structure still bears the mark of neoliberalism. Some expansion of the social welfare system took place as early as the 1970s and 1980s. Previously compulsory social insurance for mainly workers and their families through membership in industry-linked insurance funds has been reformed and supplemented with rules on, among other things. guaranteed minimum pension and the right to some social assistance. However, the compensation that is paid out often does not cover even basic supply needs. More than a third of women gain employment,
The right to health care is constitutionally established, and a relatively widespread system of general health care facilities also provides free care if needed. Resources are fairly unevenly regionally distributed. For upper and middle class, privately owned clinics and hospitals are obvious alternatives, but social insurance also gives other social strata some choices. The density of doctors is one doctor per 1,000 residents.
In August, Congress opened investigations into the origins of Pinochet’s fortune and the million account that had been discovered in the United States. A group of Chilean parliamentarians traveled to the United States to investigate his accounts there. The Chamber of Deputies also set up a commission to prepare, within a period of 120 days, a report on the financial situation of the dictator, and in particular on the circumstances of the privatization of public property undertaken under the Pinochet dictatorship. Although Parliament had already undertaken a study of these privatizations in the 1990’s, the study’s conclusions were never made public.
That same month, the publication of a picture of a Peruvian military base in Arequipa created tensions between Santiago and Lima. Chilean Defense Minister Michelle Bachelet declared that the expansion of the air base was “publicly known” in military circles. The minister urged Chilean parliamentarians to take the announcement seriously and not “whip up a mood”. She further stated that the images were not taken by the intelligence but by the Israeli company Image Sat and that the purpose was the sale of satellite services. The Peruvian Defense Minister stated that pictures were taken in December 2002 and were publicly available.
The controversy over the air base took place after disagreements in July, with Peru’s President Alejandro Toledo speaking out in favor of a revision of a maritime border demarcation agreement between the two countries of the 1950’s. Chile stated on that occasion that the agreement was not negotiable. Following Toledo’s statements, Chile carried out a military exercise that, as a scenario, had a conflict with Chile’s neighboring countries. The military leadership insisted that the exercise was planned long before the discrepancies.
On August 26, the Supreme Court handed down a ruling that, with 9 judge votes against 8, removed Pinochet’s immunity. The consequence was that the ex-dictator could then be prosecuted for his command of disappearances during Operation Condor in the 70’s and 80’s. An operation that also involved other military dictatorships in Latin America. In its ruling, the Supreme Court rejected requests from Pinochet’s defenders that the ex-dictator should not be brought to justice for health reasons.
On August 30, Brazil’s President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva refused to extradite Mauricio Hernández Norambuena to Chile, where he was wanted for abduction and murder. Lula stated that Norambuena can only be extradited once he has served his sentence for crime committed in Brazil. Acc. the Chilean authorities belong to the Norambuena rebel group Frente Patriótico Manuel Rodríguez (FPMR) who was responsible for explosives attacks during the Pinochet dictatorship. The FPMR continued its actions for several years after the transition to democracy in 1990.
In September, IMF Director Rodrigo Rato arrived in Chile to attend the 11th meeting of finance ministers in the Pacific APEC. The Summit in Santiago also included US President George Bush, as well as heads of state from Russia, China, Japan and other countries participating in the APEC cooperation. The same was true of the leaders of the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank and the Asian Development Bank. The summit discussed global and regional economic development – including capital flows between countries and countries’ economic policies. APEC consists of 21 countries, accounting for about half of the world’s production.