Niger is a country located in West Africa. It has an area of 1,267,000 square kilometers and a population of approximately 22 million people. The ethnic composition of Niger is mainly Hausa and Fulani, with other minority groups including Tuareg, Kanuri and Toubou. The majority of the population are adherents to Islam, with around 95% following the religion and the rest being either Christian or other faiths. Education is compulsory for children up to the age of 16 and the literacy rate is estimated to be around 28%. The official language is French but there are also many other languages spoken throughout the country such as Hausa, Fulfulde and Tamashek. The capital city Niamey has an estimated population of over 1 million people making it the largest city in Niger. Check hyperrestaurant to learn more about Niger in 2009.
Social conditions
Niger is one of the world’s poorest countries with high unemployment and underemployment. Visit AbbreviationFinder to see the definitions of NER and acronym for Niger. Similarly, the lack of clean water and functioning sewage systems, especially in rural areas, where only 40% of the population has access to clean water is a major problem. About 75% of the population lives in poverty (under US $ 2 per day).
| Land area | 1,267,000 km² |
| Total population | 22,772,361 |
| Residents per km² | 18th |
| Capital | Niamey |
| Official language | French |
| Income per capita | $ 1,200 |
| Currency | CFA Franc BCEAO |
| ISO 3166 code | NE |
| Internet TLD | .ne |
| License plate | RN |
| Telephone code | +227 |
| Time zone UTC | +1 |
| Geographic coordinates | 16 00 N, 8 00 O |
Health care is poorly developed with hospitals only in the larger cities; there are three hospital beds per 10,000 residents (2005). The rural population has very limited access to public health care. Physician density is among the lowest in the world, 1 per 50,000 residents (2008). Qualified personnel are available at only every three births. Vaccination programs have reduced mortality in epidemic diseases, but various infectious and parasitic diseases (lung diseases, malaria, measles, gastric diseases, whooping cough) are serious health problems and are among the most common causes of death. About 1% of the population aged 15-49 is estimated to be affected by HIV/AIDS (2009). In 2009, 14% of the state budget was allocated to health care.
Women are discriminated against in a number of ways. Abuse of women is common, but is rarely reported. Slavery is formally prohibited, but many Nigerians, especially women, still live in slave-like conditions. Genital mutilation (female genital mutilation) occurs among certain ethnic groups, but the practice is prohibited and appears to be diminishing in scope. Only about one in five women are literate, but in primary school the proportion of girls is now only slightly lower than the proportion of boys. More than 1/3 of the women are professionals. Of the country’s MPs, 13% are women. Check to see Niger population.
NIGER
The town covers an area of 1,186,408 km 2 and is divided into 8 departments where, at the 1988 census, there were 7,249,596 residents (over 8 million according to the 1991 registry estimates).
The average density of 6.1 residents / km 2 is of little significance: the population is concentrated mostly in the southern belt (from the border with Burkina Faso to that with Chad), which is the most favored area for presence of water (the Niger river to the west; Lake Chad and its tributary Komadugu to the east), while the whole northern part of the country is included in the great desert domain of the Sahara.
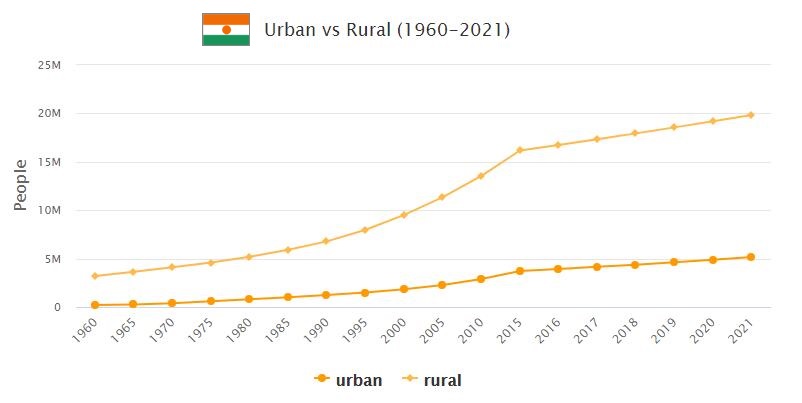
Niamey, the capital, with a river port on the Niger, has about 400,000 residents and it is the main agglomeration of the country: the urban settlement affects only 21% of the total population; the stable settlement of oases, agricultural villages and a few cities is matched by the mobility of nomadic shepherds and seasonal farmers. In order of importance, the second city is Zinder (82,800 residents), Formerly the capital of the Niger, peanut sorting center. The cities of Agadès and Arlit are susceptible to development, especially due to their proximity to the uranium mining area.
The annual growth coefficient is around 3.4% (1985-90); the rate of illiteracy is high (72%); the Muslim religion prevails over the traditional animist one (15%), while the Catholic presence is almost insignificant. From an ethnic point of view, the Hausa group dominates (52%); followed by Djerma (15%), Fulbe (10%), Kanuri (9%) and Tuareg (3%).
Only 11.7% of the national territory is used for primary activity (2.8% arable land, 7.3% meadows and pastures and 1.6% forests), which absorbs almost 40% of the active population and contributes with just over a third of the gross domestic product. In 1991, GDP per capita was around $ 300 and, in real terms, it declined at an average rate of 2.4% a year over the 1969-90 interval. At the same date, the country’s external debt amounted to $ 1.58 billion (World Bank estimates).
Agricultural production aimed at domestic consumption is modest and is based on the production of millet (18,530,000 q in 1991), sorghum (4,720,000 q), cassava (2,160,000 q), corn (60,000 q), wheat (20,000 q), yams (350,000 q). Among the crops destined for export we remember the peanut, planted by the French, which today gives increasingly reduced harvests, around 6-700.000 q per year. Small quantities of tobacco and sugar cane are also grown.
4.9 million m 3 of timber is extracted from the forest (1990); fishing from Lake Chad and the two rivers mentioned is also modest (3400 t of catch in 1990) and the dried or smoked product is sent to Nigeria.
The country’s wealth rests entirely on the subsoil, even if the mining sector occupies 5% of the population and contributes only 5.2% of the gross national product. It is above all the uranium mined in Arlit and Akouta that fuels a strong international trade; this is followed by cassiterite resources (extracted in two locations: between Zinder and Gouré and in the Air) which are exported from the port of Lagos in Nigeria. Then there are sodium phosphates in Air, in Tahoua, iron ore in Say near Niamey and in Kantch, salt in Bilma and around Agadès, gold in Koma Bangou.
The electricity production is modest, mainly of thermal origin: it is around 162 million kWh while the installed power is 63,000 kW (1989), insufficient for the installation of industrial plants of any dimensional significance. The manufacturing apparatus is centered on the agricultural sector: oil mills in Maradi, Matameye and Magaria; production of beer and processing of sugar cane in the capital where textile plants are also located; a cement factory in Malbara.
The infrastructure network is minimal: in the absence of railways, the connections take place on the road network which at the end of the 1980s had a length of 19,000 km; in the same period, there were about 35,000 vehicles on the road. Partially used the navigation on the Niger, hampered by the rapids of Gaya. Niamey and Agadès have international airports.