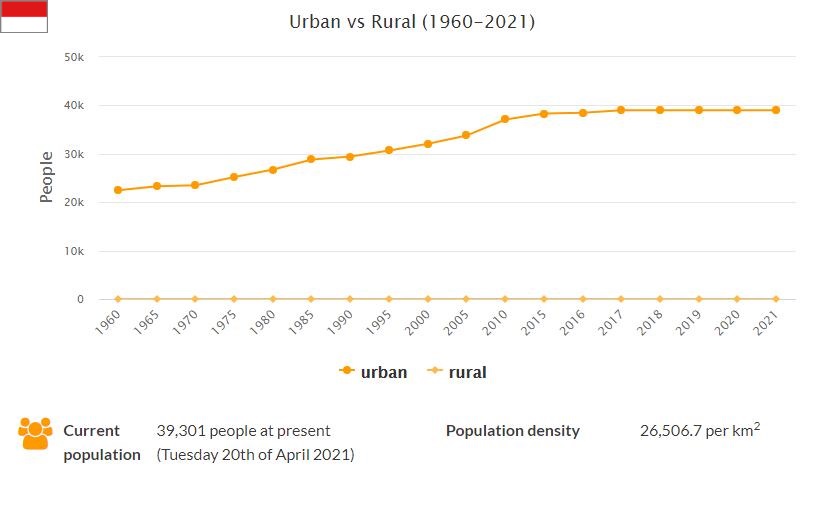
Monaco is a country located in Western Europe. It has an area of 2.02 square kilometers and a population of approximately 38,000 people. The ethnic composition of Monaco is mainly Monegasque, with other minority groups including French, Italian and British. The majority of the population are Roman Catholic Christians, with around 90% following Christianity and the rest being either other faiths or non-religious. Education is compulsory for children up to the age of 16 and the literacy rate is estimated to be around 99%. The official language is French but there are also many other languages spoken throughout the country such as English, Italian and Monegasque. The capital city Monaco has an estimated population of over 18,000 people making it the largest city in Monaco. Check hyperrestaurant to learn more about Monaco in 2009.
Social conditions
Monaco does not belong to the social welfare states. Visit AbbreviationFinder to see the definitions of MCO and acronym for Monaco. There are no general insurance systems, but the residents are expected to take care of such on their own. The state’s intervention is largely confined to running the country’s only hospital. It has a fairly high medical density (490 residents per doctor in 1994) but rather limited hospital capacity. However, this should be supplemented by several nearby private hospitals along the Côte d’Azur. Infant mortality is on a par with most Western European countries. Check to see Monaco population.
Monaco Geopolitics
The Principality of Monaco is the second smallest state in the world after the Vatican. It has its roots in the thirteenth century, when the Guelph family of the Grimaldi, following the exile imposed by the Ghibelline rulers of the Republic of Genoa, settled on the fortress of Monaco, giving life to the principality (1297). Albert II, who succeeded his father, Prince Rainier III in July 2005, is the last descendant to the throne.
The Fundamental Charter of 1962 establishes a constitutional and hereditary monarchy. The Monegasque political system provides that it is the prerogative of the prince to appoint the prime minister (defined as the ‘minister of state’) and to give him powers in matters of international relations, police and direction of governmental activity. Michel Roger, premier since March 29, 2010, is assisted by five ministers, respectively responsible for internal and external affairs, development, finance and economics, welfare and health. Legislative and budgetary power are held jointly by the prince and the National Council, made up of 24 members elected every five years. There are four municipal councils, one for each district of Monaco: La Condamine, Fontvieille, Monaco-Ville and Monte Carlo,
Tourism and financial services constitute the Monegasque economic engine. Both, however, following the crisis that hit the euro zone, were affected by the sharp decline in the influx of tourists and in sales in the real estate sector. In 2009, GDP decreased by 11.5% and the economic prospects remain tied to the fate of neighboring countries.
However, the banking centers of Monaco are among the most prosperous in the world also by virtue of the Monegasque legislation which, in addition to not providing for taxation for citizens residing in Monaco, strongly protects privacy of domestic and foreign customers, thus attracting large amounts of money that could also come from illicit sources. In 2003, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified Monaco as a tax haven and the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) blacklisted it from countries that do not cooperate in financial and banking matters. Recently the OECD placed Monaco on the so-called ‘gray list’, made up of countries that have formally committed themselves to respecting international agreements on financial matters but have nevertheless evaded them. The Principality holds the record for the country with the highest per capita rate of billionaires in the world.
On the diplomatic level, Monaco has good relations with all the countries of the region. In 1993 he joined the United Nations and since 2004 he has been a member of the Council of Europe. It has always had a privileged relationship with France, which exerts a particular influence on the politics and economy of the principality, as also revealed by the succession of French politicians at the top of the Monegasque public administration and the involvement of French companies in the most important economic projects of the principality. Among the most important agreements, the one on security, which establishes the French commitment to defend the territory of Monaco, without an army. Since 2005, with the entry into force of a new treaty, Monaco has acquired greater autonomy in foreign policy.