Morocco is a country located in North Africa. It has an area of 446,550 square kilometers and a population of approximately 35 million people. The ethnic composition of Morocco is mainly Arab-Berber, with other minority groups including African, Andalusian and Jewish. The majority of the population are adherents to Islam, with around 99% following the religion and the rest being either Christian or other faiths. Education is compulsory for children up to the age of 15 and the literacy rate is estimated to be around 67%. The official language is Modern Standard Arabic but there are also many other languages spoken throughout the country such as Berber dialects, French and Spanish. The capital city Rabat has an estimated population of over 1 million people making it the largest city in Morocco. Check hyperrestaurant to learn more about Morocco in 2009.
Social conditions
There are a number of social security benefits paid by workers and employers, but they cover only a small part of the population. Alongside these are temporary food and employment programs for the unemployed. Employment and unemployment are extensive, with around two million Moroccans working in Europe (mainly in France). At the same time, child labor is common.
| Land area | 446,550 km² |
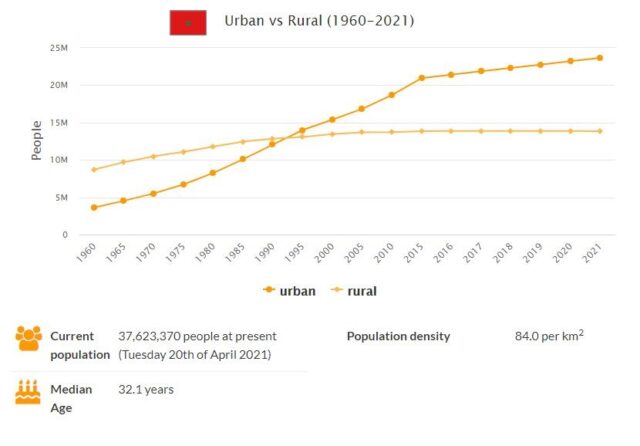
| Total population | 35,561,654 |
| Population density (per km²) | 79.6 |
| Capital | Rabat |
| Official language | Arabic |
| Income per capita | $ 8,600 |
| Currency | Moroccan dirham |
| ISO 3166 code | MA |
| Internet TLD | .ma |
| License plate | MA |
| Telephone code | +212 |
| Time zone UTC | 0 |
| Geographic coordinates | 32 00 N, 5 00 W. |
The Moroccan woman has formally the same rights as men except within the family. In recent years, however, legislative changes have strengthened the position of women, even though traditional norms remain, especially in rural areas. Almost as many girls as boys start school. Of Parliament’s members, 10% are women. Check to see Morocco population.
The differences in living standards between the city and the countryside are large, and malnutrition is a major problem in the countryside and among the urban poor. Living conditions in the Moroccan countryside are considered comparable to those prevailing in Africa’s poorest sub-Saharan countries. In 2007, 14% of the population lived in poverty (below US $ 2/day). Only 60% of rural people have access to clean water. Visit AbbreviationFinder to see the definitions of MAR and acronym for Morocco.
Health care is inadequate, especially in rural areas. Health care has deteriorated in recent years. In the past, care was free, but today the state hospitals charge. In 2009, 7% of government spending went to health care. There are eleven hospital beds and six doctors per 10,000 residents (2009). Qualified personnel are available for just under 2/3 of deliveries.